

To our eyes, the movement blurs each LED blink into a line. You just specify the device name in the initial open function. In fact, one of the most common uses of GPIO ports is to control one or more.
#WIRINGPI PORT CONTROL SERIAL#
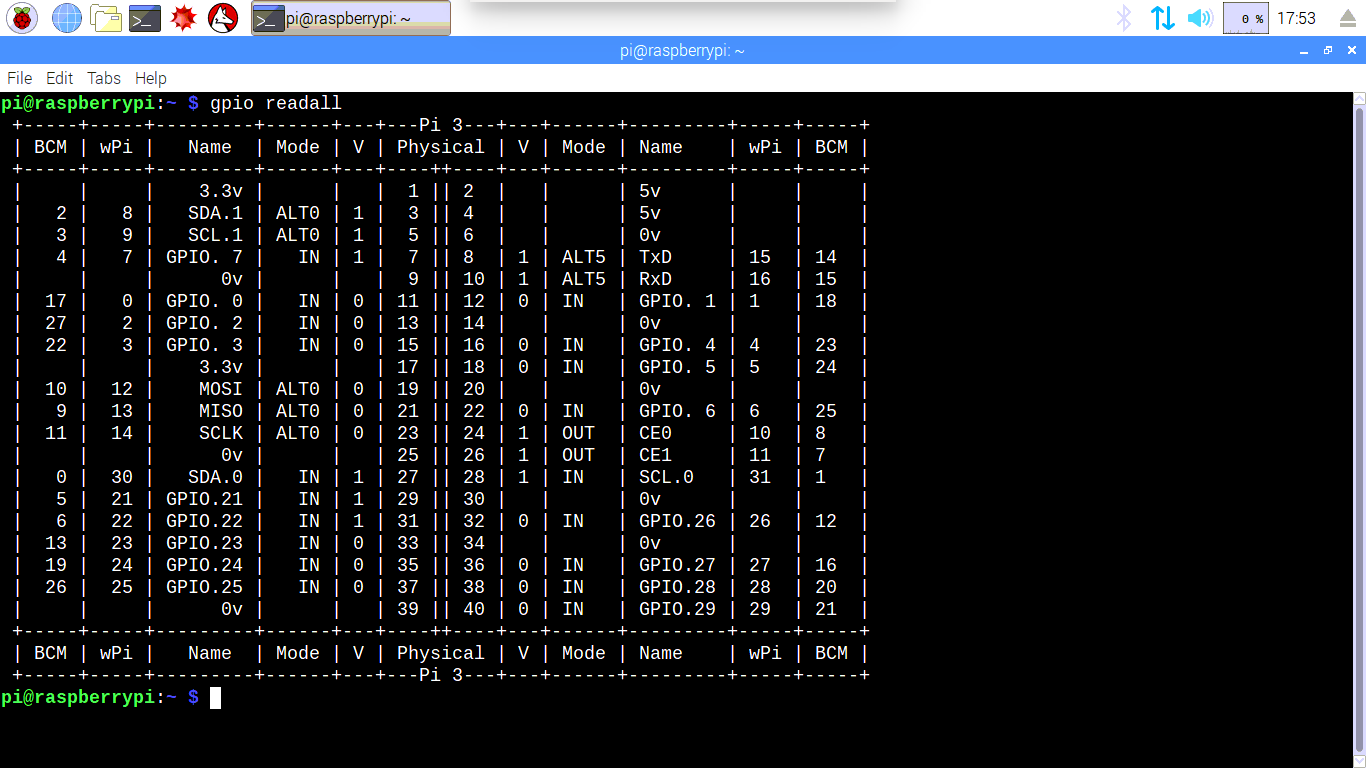
It can use the on-board serial port, or any USB serial device with no special distinctions between them. You may notice in Table 5-1 that GPIO ports 17, 18, 19, and 20 are missing. What you are doing here is essentially mapping time across the space. WiringPi includes a simplified serial port handling library. Once you get this example running, grab your arduino and shake it back and forth. To enable GPIO17 as type OUT, you can type the following.
#WIRINGPI PORT CONTROL INSTALL#
If the result looks like ‘gpio: command not found’ we need to install the WiringPi Package with the command. First check the installation of the WiringPi module with this command.
A call to analogWrite() is on a scale of 0 - 255, such that analogWrite(255) requests a 100% duty cycle (always on), and analogWrite(127) is a 50% duty cycle (on half the time) for example. Step 2: Validate the working through the WiringPi gpio module. SPI, and UART serial ports and can be used as normal ports when not multiplexed. In other words, with Arduino's PWM frequency at about 500Hz, the green lines would measure 2 milliseconds each. Finally, the Raspberry Pi receives instructions to control the. WiringPi is basically a C++ library for Raspberry Pi. Gpio can also control the popular Gertboard and the PiFace board. So you can use individual Read out and change GPIO pins in the terminal or in a bash script. This duration or period is the inverse of the PWM frequency. WiringPi, Description: WiringPi Library for Raspberry Pi GPIO Commands- The WiringPi project provides the GPIO commands. In the graphic below, the green lines represent a regular time period. If you repeat this on-off pattern fast enough with an LED for example, the result is as if the signal is a steady voltage between 0 and Vcc controlling the brightness of the LED. To get varying analog values, you change, or modulate, that pulse width. The duration of "on time" is called the pulse width.
#WIRINGPI PORT CONTROL FULL#
This on-off pattern can simulate voltages in between the full Vcc of the board (e.g., 5 V on Uno, 3.3 V on a MKR board) and off (0 Volts) by changing the portion of the time the signal spends on versus the time that the signal spends off. Digital control is used to create a square wave, a signal switched between on and off. Pulse Width Modulation, or PWM, is a technique for getting analog results with digital means. It is available in the File->Sketchbook->Examples->Analog menu of the Arduino software. The Fading example demonstrates the use of analog output (PWM) to fade an LED.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
